Tissue Expanders + ADM in Washington DC
Also Serving Mclean, Alexandria, Loudoun County and Arlington
What are tissue expanders and why would I need one?
A tissue expander (TE) is a temporary inflatable implant that a surgeon places into the breast pocket after mastectomy. If there’s a chance that you’ll need radiation, then a tissue expander is placed to act as a temporary “space holder” which is often necessary for safety reasons. For instance, if you’re planning to have a permanent silicone implant for reconstruction, it may not be safe to place this at the time of your mastectomy because of too much pressure on the breast skin. If radiation is needed and you’re planning to have a tissue flap (DIEP, love handle) procedure, then TEs prevent radiation damage to the flap. Therefore, tissue expanders provide a way to bridge the gap between stages of reconstruction. Dr. Rad will advise patients to have a tissue expander(s) for the following reasons:
- if you desire a larger final breast size as compared to your pre-mastectomy size
- if you have cancer and it remains unknown whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes (and thus whether radiation is needed).
- if you’ve had radiation in the past and now need a mastectomy
- if you’ve had reconstruction elsewhere and you’re dissatisfied with your results, then sometimes TEs are needed (but not always)
- if you would like tissue reconstruction (DIEP flap or love handle flap) but your oncologists don’t yet know whether radiation will be needed
TE have a metal port integrated within the implant and may be placed above or below the chest (pectoralis major) muscle. A drainage tube is placed and usually stays in 2-3 weeks. TE are progressively inflated or deflated in the office, and are designed to hold the breast pocket open, maintain breast shape, and prevent the skin from contracting while you finish our cancer treatments. Saline is injected painlessly into the port to fill the expander. This stretches the breast pocket in preparation for the next stage of reconstruction (either a permanent silicone implant or a flap).
TEs may be placed above or below the chest (pectoralis major) muscle. If Dr. Rad feels that placing the implant below the muscle is necessary then rest assured that your arm function will remain completely normal because the chest muscle is not used for arm or hand function. A drainage tube is placed and usually stays in 2-3 weeks. Saline can be injected painlessly into an integrated metal port to fill the expander. This stretches the breast pocket in preparation for the next stage of reconstruction (either a permanent silicone implant or a flap).
What prevents an implant from being pulled down by gravity?
What is ADM?
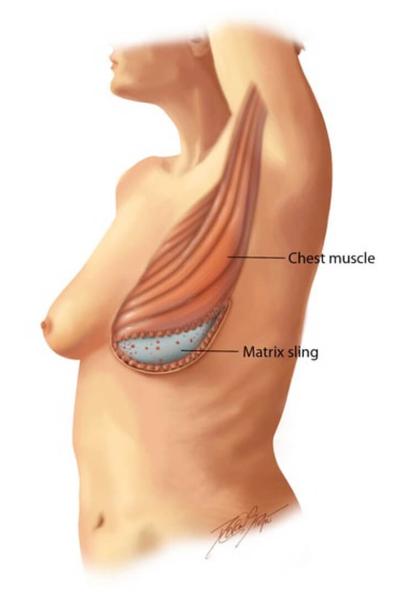
After mastectomy, all the strong support tissues holding the breast shape are removed. Unless the breast skin is reinforced, a tissue expander or implant will be pulled down by gravity. Therefore the skin must be reinforced with a strong material. This material is referred to as “acellular dermal matrix” (ADM) or “matrix sling.”
ADM is the thick dermis layer of skin taken from an organism (human or animal) and has been processed to remove all cells, then sterilized and packaged for use in surgery. It is used as a “sling” or a “hammock” to support an implant and prevent it from migrating or shifting out of place. Dr. Rad’s preferred material is Alloderm, a human-sourced ADM that has been proven through many scientific studies to be safe and effective for use in breast reconstruction. While using human skin may seem unusual, this technique is the gold standard approach to staged breast reconstruction. It also reinforces the delicate breast skin after mastectomy. The ADM material is sewn to the strong chest tissues to anchor it, and the weight of the implant is supported. Dr. Rad uses Alloderm as it has a long track record of safety as shown in multiple journal publications and Dr. Rad has published scientific studies on the use of ADM showing that it works well and is safe for use. In general, this material is only used for mastectomy patients.
What should I expect after mastectomy and tissue expander reconstruction?
It’s common to have a tightness feeling across the chest as well as temporary muscle spasms. These symptoms are normal and are controllable with pain medicine as well as a muscle relaxant. You will be kept comfortable with IV medicines the first night of surgery and then you’ll be discharged with prescription pain medicine and muscle relaxant.
It’s also common to have pins and needles sensations, twinges, pulling, or shooting electrical- type sensations particularly with movement – these are normal symptoms and they are not dangerous, nor do they indicate anything dangerous, and simply can happen because the nerves of the breast tissue are healing. If they happen with some frequency and are especially bothersome, then your medications can be adjusted to help minimize these symptoms. Otherwise, it simply takes time for these feelings to diminish.
Tissue expanders are gradually inflated in the office, and are designed to hold the breast pocket open, maintain breast shape, and prevent the skin from contracting. This is not painful.
Tissue expanders feel very firm and unnatural due to the metal port within the device, and overfilling the expander causes it to stretch and tighten. Keep in mind this feeling is temporary as the expander is designed to stretch the pocket, not feel like a natural breast.
Who is a candidate for a tissue expander?
The ideal patient for whom a tissue expander is necessary is one who may need radiation after mastectomy and she wants a her own tissue for reconstruction (DIEP Flap or Love Handle Flap). Since radiation would damage a DIEP flap or Love Handle flap, it is best to have a tissue expander first, and then after radiation undergo the DIEP flap.
 Other Options
Other Options
- Certain patients may skip tissue expander surgery if radiation will not be needed and tissue reconstruction with a DIEP Flap or Love Handle Flap is desired.
How It’s Done
- At the time of a mastectomy or for a patient who does not have a breast at all (Stage 1), Dr. Rad places a tissue expander (TE) beneath the chest muscle.
- In Stage 2, the tissue expander is removed and either a tissue reconstruction is performed or Teardrop Silicone Implant is placed.
- Click here for a more detailed description of the Stages of Reconstruction.
Safety
- Breast reconstruction surgery is done under general anesthesia.
- Dr. Rad works with a board certified anesthesiologist and performs surgery in the top hospitals in the Washington DC and northern Virginia area.
- An overnight stay is required for first stage (mastectomy and placement of tissue expander) surgery.
What to Expect
- Mild to moderate discomfort is common and is easily controlled with pain medications.
- For patients who undergo mastectomy and TE placement, recovery is about 2 to 3 weeks, and about 4 to 6 weeks to unrestricted exercise.

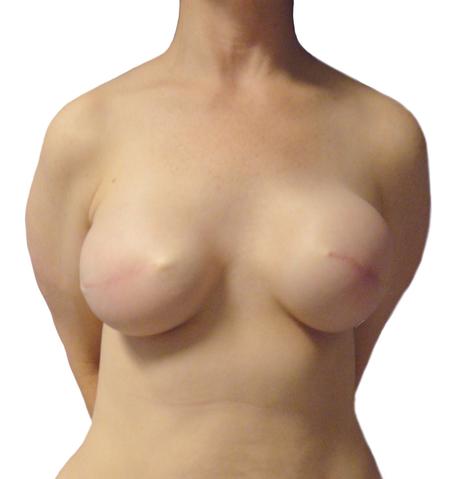
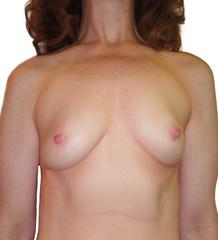
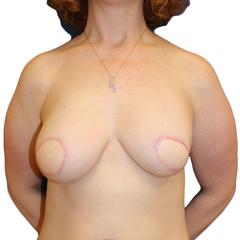
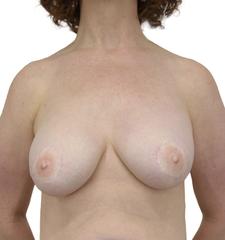
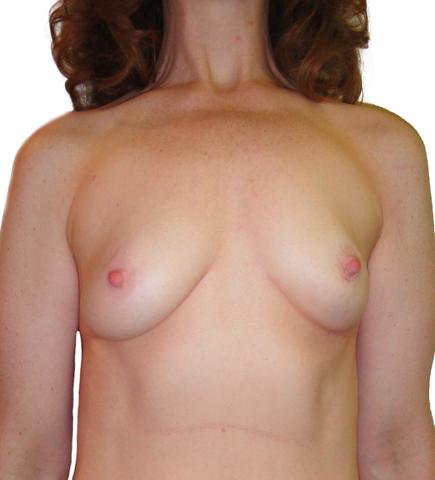
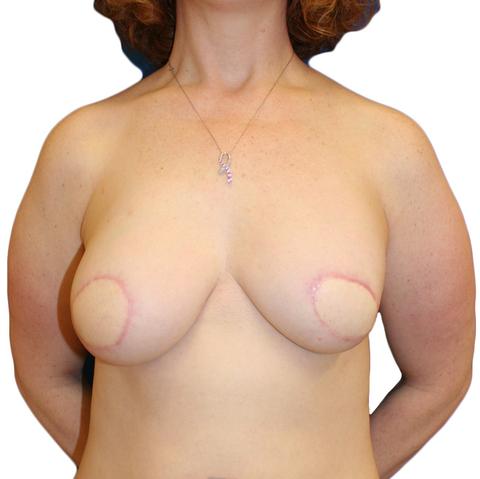
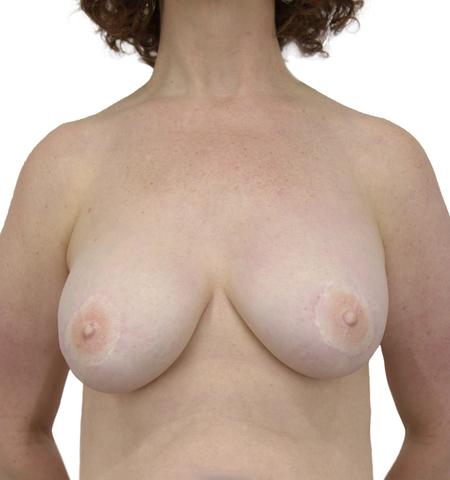
BEFORE + AFTER
This 51 year old woman underwent left mastectomy for cancer treatment, and a right prophylactic mastectomy for prevention. She underwent staged reconstruction with tissue expanders followed by LSGAP Love Handle Flaps, and Nipple Reconstruction.
Photos are of patients who have given explicit written agreement to have them displayed. For patient privacy reasons, the majority of Dr. Rad’s patients prefer their before/after photos to remain off-line. However, Dr. Rad will be happy to show you, in the setting of a confidential consultation, a series of before/after photos, not displayed here, to address your specific concerns.
*SHERBER+RAD cannot guarantee specific results. Individual results may vary.
What Patients Are Saying
“You rarely find a person who is extremely skilled and a perfectionist yet very modest, humble, sympathetic and warm hearted with a pleasant disposition. That is Dr. Rad! I was so fortunate to have found Dr. Rad, one of the very few in the country who can do Diep Flap reconstruction. Not only the reconstruction results are excellent, the pre-surgery and post-surgery care is comforting. He is always there when needed and explains every detail with lot of patience. Thank you, Dr. Rad!”
“I had a double mastectomy at Johns Hopkins in September 2014. I decided to switch to Dr. Rad because my plastic surgeon had changed the plan from DEEP flap to implants. I saw Dr. Rad for a second opinion. He was very confident that I would be a good candidate for the DEEP flap. The surgery went well. He personally came to see me after the surgery, even on the weekend. Dr. Rad was very reassuring before and after the surgery, and my recovery went exactly as he predicted. I am very pleased with the results. In addition Dr. Rad is very personable and has a great sense of humor, which can be helpful in this kind of situation. His office staff is very responsive to phone calls and is always helpful. His office environment is very friendly.”
“Dr. Rad is a plastic surgeon who is also warm and caring. He took his time explaining the surgical procedure and expected outcomes. I was diagnosed with breast cancer which required a mastectomy. Dr. Rad explained all my options for reconstruction. I chose a DIEP Flap reconstruction. After awakening from surgery and viewing my new breast, I was able to exhale. My newly constructed breast matched my existing breast perfectly.”
Dr. Rad performed my breast reconstruction with DIEP flap in 2011 after a double mastectomy. I have been absolutely thrilled with the results. He was able to do nipple and skin sparing and my breasts look great and feel very normal. I chose Dr. Rad as my plastic surgeon because he was the only one who was willing/able to do a double DIEP flap given that I am fairly thin. He stopped at nothing to get the best result possible. He has a phenomenal bedside manner and makes his patients feel totally comfortable and confident. I have recommended him without reservation to several friends for breast reconstruction and would go to him again if I needed or wanted plastic surgery.